Medical Grade Supplement Line
Vitamin B Complex
Vitamin B Complex
Couldn't load pickup availability
|
Formula Purposes & Benefits |
|
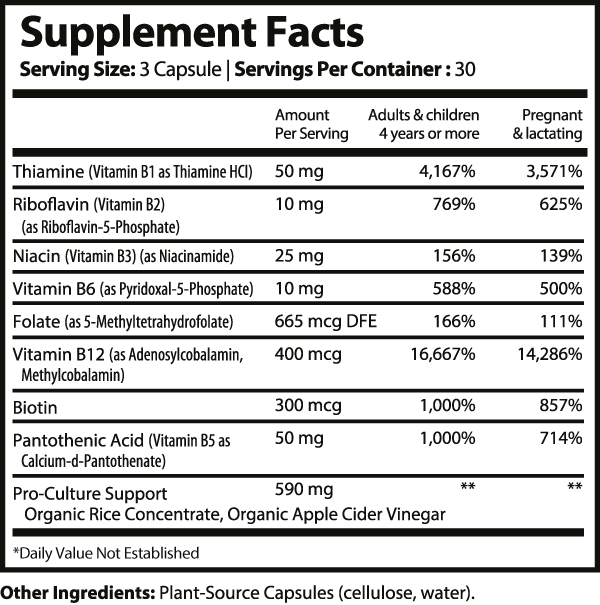
Vitamin B Complex is expertly formulated based on the latest scientific research to enhance metabolic health, boost exercise performance, and improve cognitive function. It supports a healthy immune system, promotes body fat loss, aids in hormone balance, and assists in blood cell formation. Additionally, it helps manage stress effectively, making it a comprehensive supplement for overall well-being. Vitamin B Complex offer a high-quality B vitamin formula, containing all eight essential B vitamins in their biologically active forms. These capsules deliver fully activated B vitamins directly to your bloodstream. Our formula undergoes rigorous third-party testing for heavy metals and impurities. It is proudly made in the USA in an FDA registered facility, following Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) standards. Our commitment to excellence is reflected in the fact that only 4% of the supplements on the market can match our world-class standards. |
|
Formula Ingredient Deck |
Benefits Of Each Ingredient |
|
Vitamin B-12 (Methylcynacobalamin) |
|
|
Vitamin B1 (Thiamine) |
|
|
Vitamin B-2 (Riboflavin) |
|
|
Vitamin B3 (Niacin) |
|
|
Vitamin B-6 |
|
|
Folate (as 5-Methyltetrahydrofolate)
|
|
|
Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic Acid) |
|
|
Biotin |
|
|
Pro culture support (organic rice concentrate, organic apple cider vinegar) |
|
|
Proper Use of This Supplement |
|
|
Our Formula Vs Other Formulas on the Market.
|
|
|
|
1. Uses third party independently tested ingredients that are made in the USA, GMP certified, and made in an FDA registered facility. |
1. Source cheap ingredients from heavily polluted soils. Even “organic” supplements not third party tested have been removed by FDA due to high levels of heavy metals. |
|
2. High quality B-vitamin complex in a bioavailable and efficaciously dosed formula. |
2. Uses cheap synthetic b-vitamins that may have heavy metals due to poor product quality and lack of third-party lab testing for heavy metals. |
Sources:
- Gasperi, V., Sibilano, M., Savini, I., & Catani, M. V. (2019). Niacin in the Central Nervous System: An Update of Biological Aspects and Clinical Applications. International journal of molecular sciences, 20(4), 974. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20040974
9.Gentilcore D. (2016). Louis Sambon and the Clash of Pellagra Etiologies in Italy and the United States, 1905-14. Journal of the history of medicine and allied sciences, 71(1), 19–42. https://doi.org/10.1093/jhmas/jrv002
10.Kirkland J. B. (2009). Niacin status and treatment-related leukemogenesis. Molecular cancer therapeutics, 8(4), 725–732. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-09-0042
11.Hoki, P., Rojas, A., & Saunders, M. (2009). Accelerated radiotherapy, carbogen, and nicotinamide (ARCON) in the treatment of advanced bladder cancer: mature results of a Phase II nonrandomized study. International journal of radiation oncology, biology, physics, 73(5), 1425–1431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2008.06.1950
- Ueland, P. M., McCann, A., Midttun, Ø., & Ulvik, A. (2017). Inflammation, vitamin B6 and related pathways. Molecular aspects of medicine, 53, 10–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mam.2016.08.001
- Bird R. P. (2018). The Emerging Role of Vitamin B6 in Inflammation and Carcinogenesis. Advances in food and nutrition research, 83, 151–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.afnr.2017.11.004
- Mascolo, E., & Vernì, F. (2020). Vitamin B6 and Diabetes: Relationship and Molecular Mechanisms. International journal of molecular sciences, 21(10), 3669. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21103669
- van de Lagemaat, E. E., de Groot, L., & van den Heuvel, E. (2019). Vitamin B12in Relation to Oxidative Stress: A Systematic Review. Nutrients, 11(2), 482. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11020482
- Romain, M., Sviri, S., Linton, D. M., Stav, I., & van Heerden, P. V. (2016). The role of Vitamin B12 in the critically ill--a review. Anaesthesia and intensive care, 44(4), 447–452. https://doi.org/10.1177/0310057X1604400410
- Shipton, M. J., & Thachil, J. (2015). Vitamin B12 deficiency - A 21st century perspective . Clinical medicine (London, England), 15(2), 145–150. https://doi.org/10.7861/clinmedicine.15-2-145
- Bailey, L. B., Stover, P. J., McNulty, H., Fenech, M. F., Gregory, J. F., 3rd, Mills, J. L., Pfeiffer, C. M., Fazili, Z., Zhang, M., Ueland, P. M., Molloy, A. M., Caudill, M. A., Shane, B., Berry, R. J., Bailey, R. L., Hausman, D. B., Raghavan, R., & Raiten, D. J. (2015). Biomarkers of Nutrition for Development-Folate Review. The Journal of nutrition, 145(7), 1636S–1680S. https://doi.org/10.3945/jn.114.206599
- Thakur, K., Tomar, S. K., Singh, A. K., Mandal, S., & Arora, S. (2017). Riboflavin and health: A review of recent human research. Critical reviews in food science and nutrition, 57(17), 3650–3660. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2016.1145104
- Suwannasom, N., Kao, I., Pruß, A., Georgieva, R., & Bäumler, H. (2020). Riboflavin: The Health Benefits of a Forgotten Natural Vitamin. International journal of molecular sciences, 21(3), 950. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21030950
- DiNicolantonio, J. J., Niazi, A. K., Lavie, C. J., O'Keefe, J. H., & Ventura, H. O. (2013). Thiamine supplementation for the treatment of heart failure: a review of the literature. Congestive heart failure (Greenwich, Conn.), 19(4), 214–222. https://doi.org/10.1111/chf.12037
- Saedisomeolia, A., & Ashoori, M. (2018).Thiamine in Human Health: A Review of Current Evidences. Advances in food and nutrition research, 83, 57–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.afnr.2017.11.002
- Ragaller, V., Lebzien, P., Südekum, K. H., Hüther, L., & Flachowsky, G. (2011). Pantothenic acid in ruminant nutrition: a review. Journal of animal physiology and animal nutrition, 95(1), 6–16. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0396.2010.01004.x
- Mock DM. Biotin: From Nutrition to Therapeutics. J Nutr. 2017 Aug;147(8):1487-1492. doi: 10.3945/jn.116.238956. Epub 2017 Jul 12. PMID: 28701385; PMCID: PMC5525106.
- Patel DP, Swink SM, Castelo-Soccio L. A Review of the Use of Biotin for Hair Loss. Skin Appendage Disord. 2017 Aug;3(3):166-169. doi: 10.1159/000462981. Epub 2017 Apr 27. PMID: 28879195; PMCID: PMC5582478.
- Vidmar Golja, M., Šmid, A., Karas Kuželički, N., Trontelj, J., Geršak, K., & Mlinarič-Raščan, I. (2020). Folate Insufficiency Due to MTHFR Deficiency Is Bypassed by 5-Methyltetrahydrofolate. Journal of clinical medicine, 9(9), 2836. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9092836

* These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any disease.
Share